hydrophobicity|what causes hydrophobicity : Clark In chemistry, hydrophobicity is the physical property of a molecule that is seemingly repelled from a mass of water (known as a hydrophobe). In contrast, hydrophiles are attracted to water. Hydrophobic molecules tend to be nonpolar and, thus, prefer other neutral molecules and nonpolar solvents. . See more BetGPT é o bot para visualização de sinais em tempo real.
0 · which of the following effects can occur because high surface tension water
1 · what does hydrophobicity mean
2 · what causes hydrophobicity
3 · hydrophobicity wikipedia
4 · hydrophobicity vs hydrophilicity
5 · hydrophobicity measurement
6 · hydrophobicity meaning
7 · hydrophobicity in chemicals
webJogue Pegajogos diretamente no Site de Jogos Online Gratis. Os melhores e mais novos Jogos de Pegajogos 100% grátis.
hydrophobicity*******In chemistry, hydrophobicity is the physical property of a molecule that is seemingly repelled from a mass of water (known as a hydrophobe). In contrast, hydrophiles are attracted to water. Hydrophobic molecules tend to be nonpolar and, thus, prefer other neutral molecules and nonpolar solvents. . See moreThe hydrophobic interaction is mostly an entropic effect originating from the disruption of the highly dynamic hydrogen bonds between . See more
Dettre and Johnson discovered in 1964 that the superhydrophobic lotus effect phenomenon was related to rough hydrophobic surfaces, and they developed a theoretical model based on experiments with glass beads coated with paraffin or TFE telomer. The . See more
• Froth flotation – Process for selectively separating of hydrophobic materials from hydrophilic• Hydrophile – Molecular entity that is attracted to . See moreSuperhydrophobic surfaces, such as the leaves of the lotus plant, are those that are extremely difficult to wet. The contact angles of a water droplet exceeds 150°. This is referred to . See more
Hydrophobic concrete has been produced since the mid-20th century.Active recent research on superhydrophobic materials might eventually lead to . See more
• What are superhydrophobic surfaces? See more The value −113 mJ/m 2 was proposed to be the cutoff between hydrophobicity and hydrophilicity. On the other hand, Vogler .
Learn how surfaces attract or repel water, and how this affects various technologies and applications. Find out the definitions, examples, and mechanisms of hydrophobicity and hydrophilicity, .
hydrophobicity what causes hydrophobicityThe hydrophobic effect is the observed tendency of nonpolar substances to aggregate in an aqueous solution and to be excluded by water. The word hydrophobic literally means "water-fearing", and it describes the segregation of water and nonpolar substances, which maximizes the entropy of water and minimizes the area of contact between water and nonpolar molecules. In term.
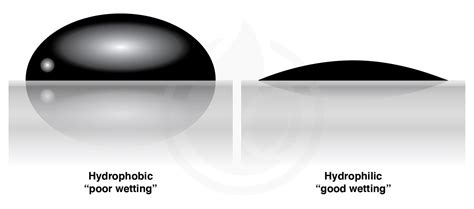
Learn about hydrophobicity, a property of molecules that determines their affinity for water and other polar solvents. Explore various applications of hydrophobicity in materials .
In general, hydrophobicity is expressed through the empirically calculated logarithm of partition coefficient (logP), which is widely used in drug design and . Hydrophobic means to fear water and refers to the property of a substance to repel water. Learn how hydrophobic molecules clump together to decrease their . Hydrophobic means "the fear of water" and refers to molecules and surfaces that repel water. Learn how hydrophobic properties affect cell membranes, plant leaves, bird feathers and more. 1. Introduction. Hydrophobicity, a key concept in chemistry, is defined by IUPAC 1 as “the association of non-polar groups or molecules in an aqueous .
The meaning of HYDROPHOBIC is of, relating to, or suffering from hydrophobia. How to use hydrophobic in a sentence. The ability of superhydrophobic surfaces to stay dry, self-clean and avoid biofouling is attractive for applications in biotechnology, medicine and heat transfer 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10.Water .Hydrophobicity is a favorable criterion for surgical tool usage. Blood, lipids, and other liquids can adhere to surgical tools if they are coated with a water-repellent coating. This improves surgeon visibility, minimizes patient blood loss, maintains equipment clean and extends their lives, and, most critically, inhibits bacterial attachment . The degree to which a surface either attracts or repels water can be termed, respectively, the hydrophilicity or the hydrophobicity of that surface. Polar liquids like water and alcohols interact more strongly with hydrophilic surfaces. Similarly, nonpolar liquids such as petroleum‐based solvents interact more strongly with hydrophobic surfaces.hydrophobicity Herein, we would like to underline the relevant water properties that strongly influence the behavior of interacting systems, mainly looking at the interplay between hydrophilicity and hydrophobicity [27]. The term “hydrophobic bonding” was first introduced by Walter Kauzmann in his attempt to explain the attraction observed . How Hydrophobicity Works . Hydrophobic molecules are nonpolar. When they are exposed to water, their nonpolar nature disrupts hydrogen bonds between water molecules, forming a clathrate-like structure on their surface. The structure is more ordered than free water molecules.
Hydrophobicity (or lipophilicity) is a well-known and extensively studied phenomenon. It is commonly understood to be the tendency of non-polar molecules to form aggregates in order to reduce their surface of contact with polar molecules such as water . Its manifestations include simple observable macroscopic phenomena such as the . Hydrophobic molecules. Water, H 2 O {H}_{2}O H 2 O, is a polar molecule, meaning it has polarity, which is an uneven distribution of electron density among its atoms.The oxygen side of any water molecule is slightly negative, while the hydrogen side is slightly positive. Polar water does not bond with nonpolar or hydrophobic molecules. .Hydrophobicity scales. Hydrophobicity scales are values that define the relative hydrophobicity or hydrophilicity of amino acid residues. The more positive the value, the more hydrophobic are the amino acids located in that region of the protein. These scales are commonly used to predict the transmembrane alpha-helices of membrane proteins.Belmont, CA: Thomas Brooks/Cole. 2005. 15. 13.6: Hydrophobic Interaction is shared under a CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by LibreTexts. Hydrophobic interactions describe the relations between water and hydrophobes (low water-soluble molecules). Hydrophobes are nonpolar molecules and usually have a long chain .

1. Introduction. Hydrophobicity, a key concept in chemistry, is defined by IUPAC 1 as “the association of non-polar groups or molecules in an aqueous environment which arises from the tendency of water to exclude non-polar molecules”. IUPAC also defines hydrophobic interactions as “The tendency of hydrocarbons (or of lipophilic .
Figure 1: The intrinsic hydrophobicity of lanthanide rare-earth oxides 2. a, Metal oxides are typically hydrophilic because their electronic structure favours the formation of hydrogen bonds. For .what causes hydrophobicityBiomimetic nanosurfaces with distinct wettability and versatility have found special enthusiasm in both fundamental research and industrial applications. With the advent of nanotechnology, it is doable to acclimate surface architecture and surface chemistry to attain superhydrophobicity. The uniqueness of superhydrophobic surfaces arises from .6.6: Hydrophobic Interactions. Hydrophobic interactions describe the relations between water and hydrophobes (low water-soluble molecules). Hydrophobes are nonpolar molecules and usually have a long chain of carbons that do not interact with water molecules. The mixing of fat and water is a good example of this particular interaction.Several hydrophobic surfaces rely on natural nanofabrication. Hydrophobicity, as already discussed (Kalaskar et al., 2008), improves encourages fibroblasts in contact with biomaterials to develop correct extended structures.Hydrophobic nanosurfaces are ubiquitous in nature, and are found, for example, on the waxy leaves of water borne .
WEBCriminal Minds. Temporada 11. "Criminal Minds" gira em torno de uma equipe de elite de analistas do FBI que estudam as mentes criminosas mais doentias do país, .
hydrophobicity|what causes hydrophobicity